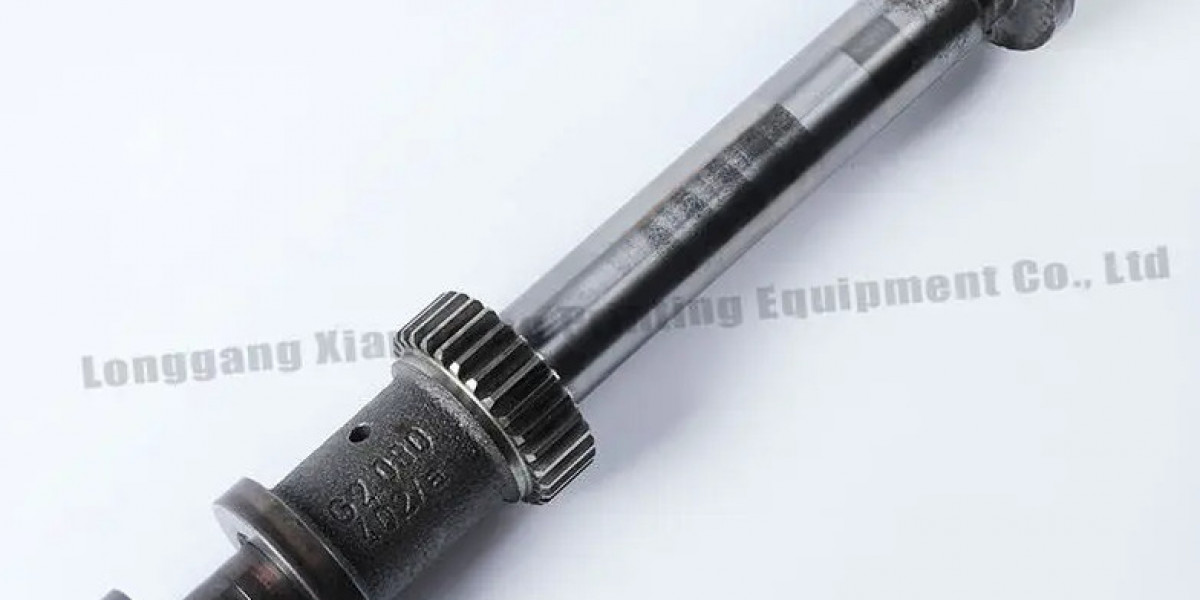
Printing Machine Gear assemblies influence how accurately mechanical motion is transmitted within printing equipment. From feeder units to impression cylinders, Printing Machine Gear performance affects registration stability and timing consistency throughout the printing process.
High-speed printing lines rely on synchronized movement between multiple rotating components. Gears act as mechanical links that maintain consistent angular relationships between these components. When gear tolerances are well controlled, the machine can maintain predictable motion even during extended production shifts.
Manufacturing quality plays a significant role in gear performance. Precision machining and surface finishing help maintain tooth accuracy and smooth engagement. Surface hardening treatments support resistance to wear, especially in environments where gears operate continuously for several thousand hours per year.
Energy efficiency is also connected to gear behavior. Reduced friction during engagement supports smoother power transmission and stable rotational speed. This helps minimize energy losses caused by unnecessary resistance or vibration during operation.
Lubrication supports these outcomes by maintaining a protective film between mating surfaces. Proper lubrication reduces metal-to-metal contact and stabilizes operating temperatures. Regular monitoring allows maintenance teams to detect deviations that could indicate misalignment or surface wear.
Gear inspection routines often focus on noise, vibration, and lubrication condition. These indicators provide early signals of performance changes. Predictable wear patterns allow maintenance planning without disrupting production schedules.
In conclusion, Printing Machine Gear accuracy supports stable registration, smooth motion transfer, and predictable operation. Through careful design, material selection, and routine monitoring, Printing Machine Gear systems help printing equipment maintain consistent performance over time.