Market Overview and Growth Dynamics
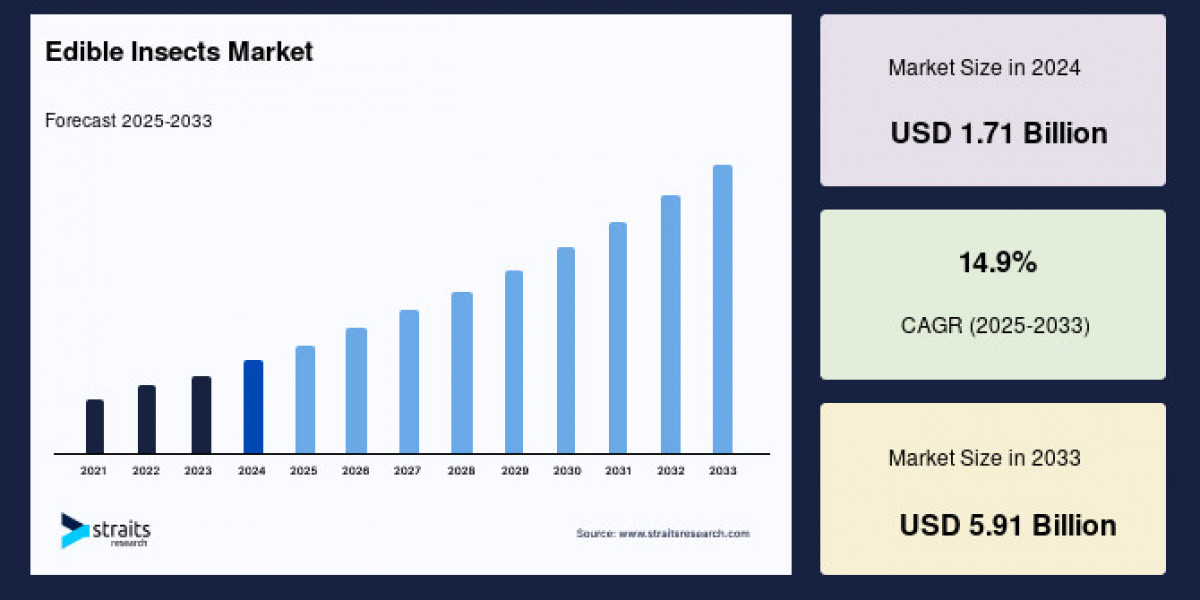
The global edible insects market size was valued at USD 1.71 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 1.95 billion in 2025 to USD 5.91 billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 14.9% during the forecast period (2025–2033). The growth of the market is attributed to sustainability and protein security.
The foundation of this market's growth lies in the intrinsic benefits of edible insects, notably their high protein content, rich micronutrient profile, minimal environmental footprint, and efficient conversion ratios compared to traditional livestock. Insects such as crickets, mealworms, grasshoppers, and black soldier fly larvae are gaining traction as viable protein sources across human nutrition, animal feed, and pet food industries. The sector is also bolstered by increasing investments in innovative farming technologies and evolving regulatory landscapes favoring insect-based products.
Drivers Shaping Market Expansion
At the core of the edible insects market is the imperative for sustainable protein solutions. Insects require up to 12 times less feed than cattle and generate substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions—nearly 100 times fewer—making them an ecologically responsible alternative. Moreover, insect farming capitalizes on organic waste streams to create protein-rich biomass, contributing to circular economy frameworks while minimizing agricultural CO₂ emissions.
Nutritionally, edible insects boast up to 70% protein content by dry weight, supplemented by essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. These attributes position insects as critical resources for addressing protein deficiencies and malnutrition globally, particularly in developing regions where protein scarcity is prevalent.
Substantial market growth is also energized by the diversification of edible insect applications. Beyond direct human consumption, insect protein is increasingly incorporated into snack bars, protein powders, baked goods, and beverages. Additionally, the animal feed sector is a lucrative segment, with insect proteins offering sustainable, cost-effective alternatives to fishmeal and soy in poultry, aquaculture, and pet foods. In particular, black soldier fly larvae are extensively employed for aquafeed in Asia and Europe, demonstrating notable environmental and economic benefits.
Regional Market Insights
Europe currently leads the global edible insects market, capturing over 38% of market share in 2025. European growth is supported by advanced consumer awareness, progressive regulatory approval of key insect species under novel food regulations, and a robust food innovation ecosystem. Key European players operate large-scale vertical insect farms, ensuring quality control across production, processing, and distribution. Countries such as France, the Netherlands, and Belgium are hotbeds of commercial insect farming activity.
North America emerges as the fastest-growing regional market with an estimated CAGR of 17.8%. In the United States, growing eco-consciousness, favorable regulatory trends, and expanding investments in food tech startups are driving increased adoption of insect-based foods. However, overcoming cultural aversion remains a challenge, with surveys indicating limited willingness among some consumers to regularly consume insects.
Asia-Pacific holds strategic significance due to longstanding cultural acceptance and practices of entomophagy in countries like Thailand, Vietnam, South Korea, and China. The region represents roughly 24% of the market in 2025 and is witnessing modernization of insect farming through governmental support programs that professionalize production and establish global supply chain networks.
Product Segment and Application Trends
Product-wise, insect powder dominates the edible insect market segment, favored for its versatility, nutritional density, and ease of integration into diverse products. Powdered insect protein coats the market in energy bars, smoothies, bakery products, pasta, and cereals, catering especially to Western consumers who may reject whole insects due to cultural reasons. The powder form effectively masks insect identity, boosting acceptance and market penetration.
Insect types such as black soldier fly larvae lead the segment for animal feed applications due to their remarkable capability to convert organic waste into high-quality protein, with a conversion rate of one ton of food waste resulting in approximately 250 kilograms of biomass. This unique aspect aligns with environmental sustainability goals and zero-waste strategies embraced by food manufacturers and feed producers.
The animal feed application notably represents the largest segment in edible insects, driven by the need for alternative, sustainable feeds in poultry, aquaculture, and pet food markets. Increasing demand for insect protein in feed caters to the dual objectives of cost reduction and carbon footprint minimization in livestock operations. Startups and established companies focus on innovative feed solutions that are scalable and comply with environmental regulations.
Challenges and Market Restraints
Despite positive prospects, the edible insects market faces significant hurdles. Cultural resistance, particularly in Western and Middle Eastern countries, remains a primary barrier, with many consumers exhibiting disgust or psychological aversion toward insect consumption. Safety concerns, allergenicity issues, and regulatory complexities surrounding labeling and approval processes slow product market entry and broader acceptance.
Retailers in some regions are reluctant to stock insect-based items due to perceived low consumer demand and turnover risks. Additionally, fragmented regulations and lack of harmonization across countries complicate cross-border trade and product launches. The industry is also challenged by the need to scale production efficiently while maintaining quality and cost competitiveness.
Future Outlook and Opportunities
The edible insects market is poised for transformative growth with expanding innovation in product development and farming practices. Emerging trends include the launch of insect-based food and beverage products designed to appeal to mainstream consumers seeking health and sustainability benefits. Brands focus on palatable formulations such as cricket protein bars, insect-enriched pasta, and baked goods that conceal the insect origin, mitigating consumer reluctance.
Integration of insect protein into premium pet food lines is another rapidly expanding frontier, driven by pet owners’ preference for hypoallergenic, eco-friendly nutrition options. Collaborations between food manufacturers, agricultural firms, and technology providers foster ecosystem development and drive market scalability.
Technological advancements such as automation in insect farming, enhanced processing techniques, and increased R&D investment will support the market’s maturation. Supportive policies and public-private partnerships are anticipated to catalyze growth, particularly in regions demonstrating regulatory openness.
In conclusion, the edible insects market represents a compelling solution to global protein security challenges and sustainability imperatives. With rising consumer interest, expanding applications, and favorable environmental credentials, edible insects are transitioning from niche alternatives to mainstream food and feed ingredients in the coming decade.